AM TRANSMITTER
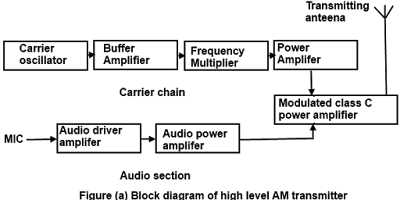
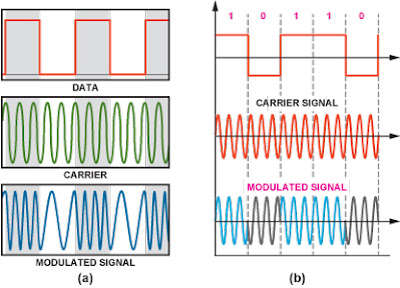
AM TRANSMITTER In an AM ( amplitude modulation ) transmitter the amplitude (strength) of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the modulation signal. In an FM (frequency modulation) transmitter the frequency of the carrier is varied by the modulation signal. There are two basic configuration for transmitters. High level modulation low level modulation High level modulation In high power modulation signal,the carrier voltage is modulated at highest power level.the require power level is obtained by class c power amplifier.The block diagram of high level modulation as shown in fig(a). low level modulation In the low level modulation system, the carrier is modulated at low power level and the carrier power is subsequently raised to the desire level in the class B amplifier . transmitters using high power level are widely use at present .The block diagram of high level modulation as shown in fig(b). ...